Atrial Flutter: Difference between revisions
m (→Examples) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
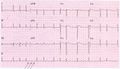
Image:aflutr_ecg.jpg|An example of an alternating 2:1 and 3:1 block. | Image:aflutr_ecg.jpg|An example of an alternating 2:1 and 3:1 block. | ||
Image:ECG_Aflutt.jpg|Atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction. | Image:ECG_Aflutt.jpg|Atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction. | ||
Image:ECG_Aflutt_1to1.jpg|Atrial flutter with 1:1 conduction (extremely rare) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 20:37, 22 July 2007
| This is part of: Supraventricular Rhythms |
| {{{locatieafbeelding}}} | |
| Atrial rate | 250-350 bpm |
| Ventricular rate | 75-150bpm (3:1 of 2:1 block) |
| Regularity | regular (sometimes changing block) |
| Origin | atrial (SVT) |
| P-wave | negative sawtooth in lead II |
| Effect of adenosine | temporary reduced AV conduction (eg 4:1) |
| Example ECG: {{{example}}} | |
| Example ECG2: {{{example2}}} | |
During atrial flutter the atria depolarize in an organized circular movement. This is caused by re-entry. The atria contract typically at around 300 bpm, which results in a fast sequence of p-waves in a sawtooth pattern on the ECG. For most AV-nodes this is way to fast to be able to conduct the signal to the ventricles, so typically there is a 2:1, 3:1 or 4:1 block, resulting in a ventricular frequency of 150, 100 or 75 bpm respectively. Often the grade of block changes every couple of beats, resulting in e.g. 2:1, or 3:1 blocks and a somewhat irregular ventricular heart rate. The saw-tooth is especially prominent in lead II, this lead normally shows constant electrical activity: it is never horizontal. Causes and risk of atrial flutter are comparable to atrial fibrillation.