Approach to Tachy-arrhythmias
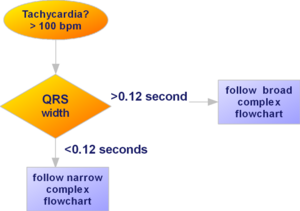
Tachy-arrhythmias are fast (tachy) i.e. > 100 bpm. Tachy-arrhythmias can be subdevided depending on their origin. They are either a:
- supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) originating from the atria or AV node, or a
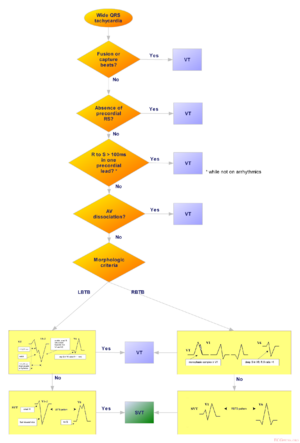
- ventricular tachycardia (VT), originating from the ventricles
To systematically get to the diagnosis of a tachycardia one has to follow the approach to the tachy-arrhythmia flow-chart.
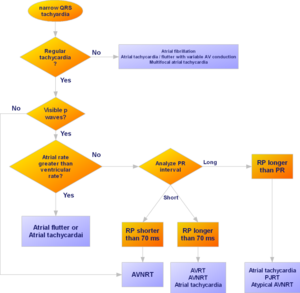
Flowchart of the approach to a narrow complex tachycardia. Adapted from [1].
Some tachycardias pass by or have their origin in the AV-node (AVRT, atrial flutter, AVNRT, AVRT etc.). Therefore blocking the AV node (by using carotic sinus massage, a valsalva manoeuvre or adenosine) can be very helpful in the diagnosis or even restore sinus rhythm. Therefore the effect of adenosine is marked in the tables below.