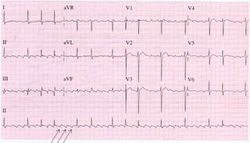
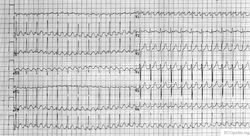
Atrial Flutter
During atrial flutter the atria depolarize in an organized circular movement. This is caused by re-entry. The atria contract typically at around 300 bpm, which results in a fast sequence of p-waves in a sawtooth pattern on the ECG. For most AV-nodes this is way to fast to be able to conduct the signal to the ventricles, so typically there is a 2:1, 3:1 or 4:1 block, resulting in a ventricular frequency of 150, 100 or 75 bpm respectively. Often the grade of block changes every couple of beats, resulting in e.g. 2:1, or 3:1 blocks and a somewhat irregular ventricular heart rate. The saw-tooth is especially prominent in lead II, this lead normally shows constant electrical activity: it is never horizontal. Causes and risk of atrial flutter are comparable to atrial fibrillation.