Sinus Node Rhythms and Arrhythmias
<analytics uacct="UA-807577-6"></analytics>
This part is about the normal ECG. The normal heart rhythm is sinus rhythm. That means that the rhythm has its origin in the sinal node, the heart's fastest physiological impulse generator.
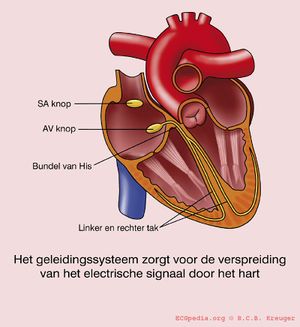
The sinus node (SA) is located in the upper part of the wall of the right atrium. When the sinus node generates an electrical impulse, first the cells of the right atrium depolarise, then the cells of the left atrium, the AV (atrioventricular) node follows and at last the ventricles are stimulated via the His bundle.
With this knowledge it is quite simple to recognise normal sinus rhythm on the ECG.
The properties of normal sinus rhythm (see also Basics):
- A P-wave (atrial contraction) precedes the QRS complex
- Every P is followed by a QRS complex
- The rhythm is regular, but varies slightly while breathing
- The frequency ranges between 60 and 100 beats per minute
- The P-waves maximum height is 2.5mm in II and/or III
- The P-wave is positive in I and II, and biphasic in V1
These last two definitions will be discussed in the topic P-top morphology.
Heart rhythms which are no sinus rhythm will be discussed in the topic rhythm disorders.