Intraventricular Conduction: Difference between revisions
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|Supervisor= | |Supervisor= | ||
}} | }} | ||
=Conduction delay= | |||
[[Image:geleidingssysteem.jpg|thumb| If the conduction system is dysfunctional, the QRS widens beyond 0.12 seconds.]] | [[Image:geleidingssysteem.jpg|thumb| If the conduction system is dysfunctional, the QRS widens beyond 0.12 seconds.]] | ||
If the QRS complex is wider than 0.12 seconds this is mostly caused by a delay in the conduction tissue of one of the bundle branches: | If the QRS complex is wider than 0.12 seconds this is mostly caused by a delay in the conduction tissue of one of the bundle branches: | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
*[[#Left_Posterior_Fasicular_Block_.28LPFB.29| Left posterior fascicular block (LPFB)]] | *[[#Left_Posterior_Fasicular_Block_.28LPFB.29| Left posterior fascicular block (LPFB)]] | ||
Sometimes this conduction delay is ''' | Sometimes this conduction delay is '''rate-dependent ''': the bundle branch block occurs only at higher heart rates and disappears at slower heart rates. | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
= LBBB vs RBBB = | |||
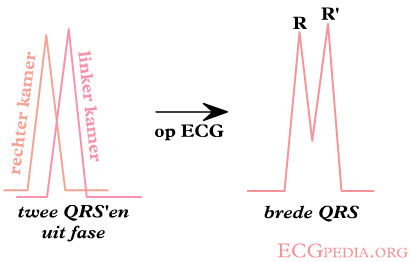
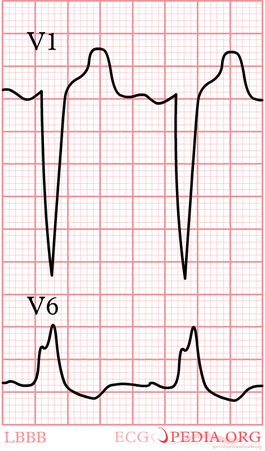
[[Image:LBTB_RBTB_en.png|thumb| A bundle branch block causes a delay in the depolarization of the right (RBBB) or left (LBBB) ventricle. In RBBB the QRS complex shows a second peak or R' in V1.]] | [[Image:LBTB_RBTB_en.png|thumb| A bundle branch block causes a delay in the depolarization of the right (RBBB) or left (LBBB) ventricle. In RBBB the QRS complex shows a second peak or R' in V1.]] | ||
Check V1 when QRS > 0.12 sec. | Check V1 when QRS > 0.12 sec. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 25: | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
=Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)= | |||
{{:LBBB}} | {{:LBBB}} | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
=Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)= | |||
{{:RBBB}} | {{:RBBB}} | ||
=Left Anterior Fascicular Block (LAFB)= | |||
{{Box| | {{Box| | ||
;Criteria for | ;Criteria for Left Anterior Fascicular Block | ||
#Frontal plane axis between −45° and −90°. | |||
#qR pattern in lead aVL. | |||
#R-peak time in lead aVL of 45 ms or more. | |||
#QRS duration less than 120 ms. | |||
These criteria do not apply to patients with congenital heart disease in whom left-axis deviation is present in infancy. | |||
}} | }} | ||
[[Image:LAHB.png|thumb|Left anterior hemiblock]] | [[Image:LAHB.png|thumb|Left anterior hemiblock]] | ||
| Line 47: | Line 46: | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
=Left Posterior Fasicular Block (LPFB)= | |||
[[File:E0003194.png|thumb|A patient with [[RBBB]] and left posterior Fascicular block]] | |||
{{Box| | {{Box| | ||
;Criteria for posterior fascicular block: | ;Criteria for posterior fascicular block: | ||
#Frontal plane axis between 90° and 180° in adults. Owing to the more rightward axis in children up to 16 years of age, this criterion should only be applied to them when a distinct rightward change in axis is documented. | |||
#rS pattern in leads I and aVL. | |||
#qR pattern in leads III and aVF. | |||
#QRS duration less than 120 ms. | |||
:Right ventricular [[hypertrophy]] and previous [[Ischemia#Lateral|lateral myocardial infarction]] have been excluded | :Right ventricular [[hypertrophy]] and previous [[Ischemia#Lateral|lateral myocardial infarction]] have been excluded | ||
}} | }} | ||
=Mechanisms of aberrant conduction= | |||
[[Image:E000573.jpg|Rate dependant left bundle branch aberration|thumb]] | |||
{{box| | {{box| | ||
;Aberrant ventricular conduction is defined as | ;Aberrant ventricular conduction is defined as | ||
| Line 84: | Line 86: | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
{{Box| | {{Box| | ||
=References= | |||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#Garcia isbn=0763722464 | #Garcia isbn=0763722464 | ||
Latest revision as of 06:08, 19 December 2012
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Moderator | T.T. Keller | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
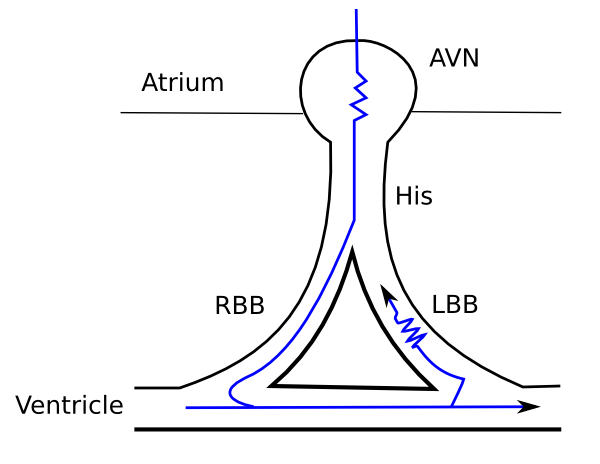
Conduction delay
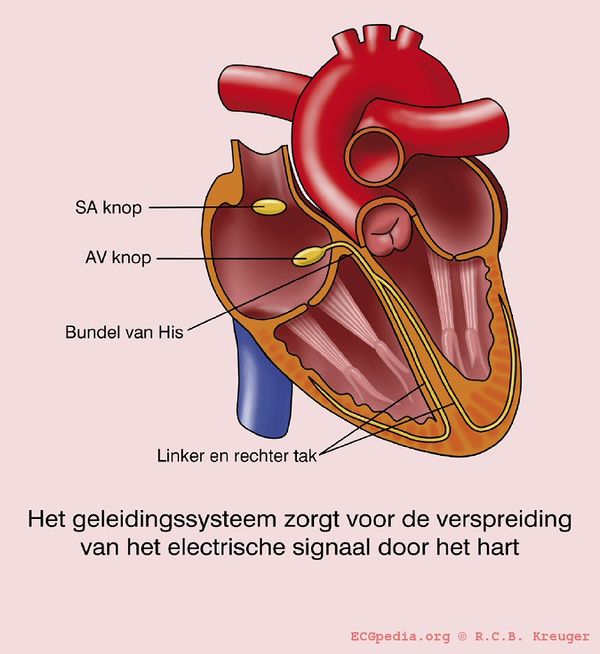
If the QRS complex is wider than 0.12 seconds this is mostly caused by a delay in the conduction tissue of one of the bundle branches:
- Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB))
- Right Bundle Branch Block(RBBB)
- Intraventricular conduction delay
A right or left axis rotation can be caused by a:
Sometimes this conduction delay is rate-dependent : the bundle branch block occurs only at higher heart rates and disappears at slower heart rates.
LBBB vs RBBB

Check V1 when QRS > 0.12 sec.
When the "terminal force" of the QRS in V1 is below the baseline (i.e. QS wave), a LBBB is the most likely diagnosis.
When the "terminal force" of the QRS in V1 is above the baseline (i.e. RSR' wave), it's a RBBB.
If the QRS > 0.12 sec. but the morphological criteria of LBBB or RBBB do not apply, it is called 'intraventriculair conduction delay', a general term.
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)
- Criteria for left bundle branch block (LBBB) Garcia
- QRS >0,12 sec
- Broad monomorphic R waves in I and V6 with no Q waves
- Broad monomorphic S waves in V1, may have a small r wave
In left bundle branch block (LBBB) the conduction in the left bundle is slow. This results in delayed depolarization of the left ventricle, especially the left lateral wall. The electrical activity in the left lateral wall is unopposed by the usual right ventricular electrical activity. The last activity on the ECG thus goes to the left or away from V1. Once you remember this, LBBB is easy to understand.
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction in LBBB can be difficult.
Other definitions
The above definition of left bundle branch block is rather broad. In selecting patients for CRT-D therapy (cardiac resynchronization therapy) there has been debate whether a more specific definition should be used. In the RAFT trial the following AHA/ESC definition was usedTangESC-ECG:
Complete LBBB
- QRS duration greater than or equal to 120 ms in adults, greater than 100 ms in children 4 to 16 years of age, and greater than 90 ms in children less than 4 years of age.
- Broad notched or slurred R wave in leads I, aVL, V5, and V6 and an occasional RS pattern in V5 and V6 attributed to displaced transition of QRS complex.
- Absent q waves in leads I, V5, and V6, but in the lead aVL, a narrow q wave may be present in the absence of myocardial pathology.
- R peak time greater than 60 ms in leads V5 and V6 but normal in leads V1, V2, and V3, when small initial r waves can be discerned in the above leads.
- ST and T waves usually opposite in direction to QRS.
- Positive T wave in leads with upright QRS may be normal (positive concordance).
- Depressed ST segment and/or negative T wave in leads with negative QRS (negative concordance) are abnormal.
- The appearance of LBBB may change the mean QRS axis in the frontal plane to the right, to the left, or to a superior, in some cases in a rate-dependent manner.
Incomplete LBBB
- QRS duration between 110 and 119 ms in adults, between 90 and 100 ms in children 8 to 16 years of age, and between 80 and 90 ms in children less than 8 years of age.
- Presence of left ventricular hypertrophy pattern.
- R peak time greater than 60 ms in leads V4, V5, and V6.
- Absence of q wave in leads I, V5, and V6.
Also a narrow initial R wave in V1 has been linked with a reduced response to CRT.Mascioli
In general when the QRS is wide and the definitions of LBBB and RBBB are not met, the term NIVCD (non-specific intraventricular conduction delay) is used.
Also read right bundle branch block.
Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
- Criteria for right bundle branch block (RBBB)
- QRS >0,12 sec
- Slurred S wave in lead I and V6
- RSR'-pattern in V1 where R' > R
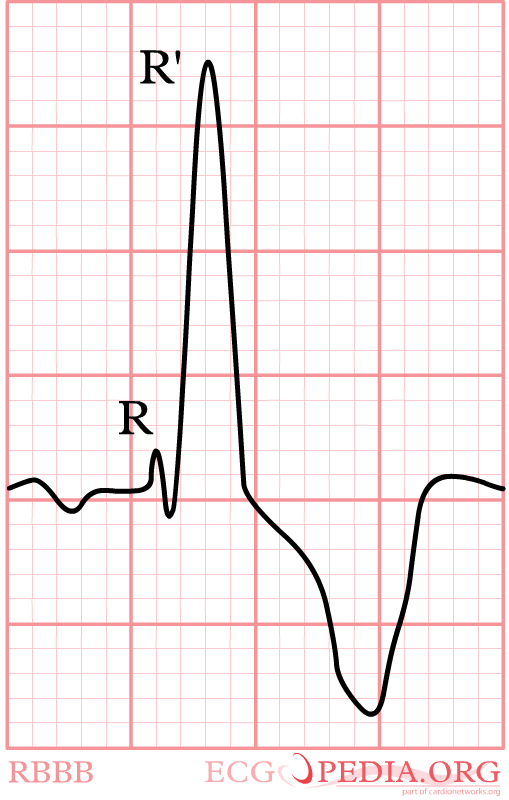

Again, watch V1. In right bundle branch block (RBBB) the conduction in the bundle to the right ventricle is slow. As the right ventricles depolarizes, the left ventricle is often halfway finished and few counteracting electrical activity is left. The last electrical activity is thus to the right, or towards lead V1. In RBBB the QRS complex in V1 is always markedly positive. RBBB is a common finding in healthy individuals. In a recent analysis of 43401 military conscripts, 13.5% had RBBB rbbb
Diagnosing myocardial infarction in RBBB is not as difficult as in LBBB.
More specific definitions
A more specific definition of RBBB is given by the ACC/ESC consensus documentESC-ECG:
Complete RBBB
- QRS duration greater than or equal to 120 ms in adults, greater than 100 ms in children ages 4 to 16 years, and greater than 90 ms in children less than 4 years of age.
- rsr′, rsR′, or rSR′ in leads V1 or V2. The R′ or r′ deflection is usually wider than the initial R wave. In a minority of patients, a wide and often notched R wave pattern may be seen in lead V1 and/or V2.
- S wave of greater duration than R wave or greater than 40 ms in leads I and V6 in adults.
- Normal R peak time in leads V5 and V6 but greater than 50 ms in lead V1.
Of the above criteria, the first 3 should be present to make the diagnosis. When a pure dominant R wave with or without a notch is present in V1, criterion 4 should be satisfied.
Incomplete RBBB
Incomplete RBBB is defined by QRS duration between 110 and 120 ms in adults, between 90 and 100 ms in children between 4 and 16 years of age, and between 86 and 90 ms in children less than 8 years of age. Other criteria are the same as for complete RBBB. In children, incomplete RBBB may be diagnosed when the terminal rightward deflection is less than 40 ms but greater than or equal to 20 ms. The ECG pattern of incomplete RBBB may be present in the absence of heart disease, particularly when the V1 lead is recorded higher than or to the right of normal position and r′ is less than 20 ms.
The terms rsr′ and normal rsr′ are not recommended to describe such patterns, because their meaning can be variously interpreted. In children, an rsr′ pattern in V1 and V2 with a normal QRS duration is a normal variant.
{{{1}}}
Left Anterior Fascicular Block (LAFB)
- Criteria for Left Anterior Fascicular Block
- Frontal plane axis between −45° and −90°.
- qR pattern in lead aVL.
- R-peak time in lead aVL of 45 ms or more.
- QRS duration less than 120 ms.
These criteria do not apply to patients with congenital heart disease in whom left-axis deviation is present in infancy.
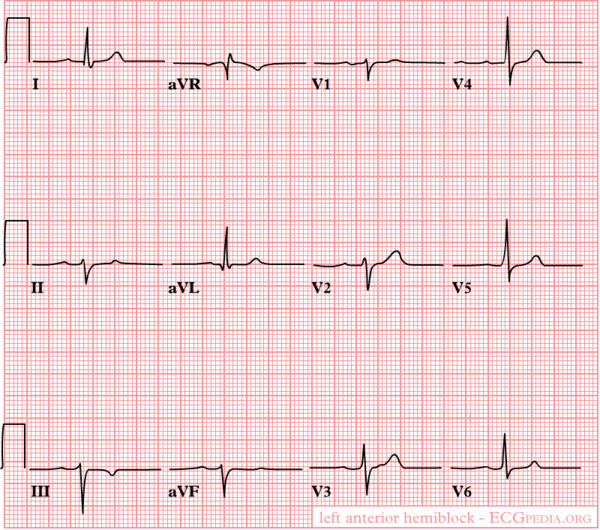
In left anterior fascicular block the anterior part (fascicle) of the left bundle is slow. This results in delayed depolarization of the upper anterior part of the left ventricle. On the ECG this results in left axis deviation. The QRS width is <0.12 seconds in isolated LAFB.
Left Posterior Fasicular Block (LPFB)
- Criteria for posterior fascicular block
- Frontal plane axis between 90° and 180° in adults. Owing to the more rightward axis in children up to 16 years of age, this criterion should only be applied to them when a distinct rightward change in axis is documented.
- rS pattern in leads I and aVL.
- qR pattern in leads III and aVF.
- QRS duration less than 120 ms.
- Right ventricular hypertrophy and previous lateral myocardial infarction have been excluded
Mechanisms of aberrant conduction

- Aberrant ventricular conduction is defined as
- QRS widening due to delay or block in bundle branch or intramyocardial conductionwellens
Mechanisms of aberration:
- Phase 3 aberration
- Phase 4 abberation or deceleration dependant
- Acceleration dependant
- Retrograde invasion
- Fixed block
Right bundle branch block is more common, because the right bundle has the longer refractory period. Left bundle branch block accounts for about 1/3rd of cases.
Phase 3 Aberration

Phase 3 aberration occurs when conduction fibers receive a new impulse, before they have fully repolarized. A premature impulse is encroaching on the refractory period of the bundle branch. This is a physiological phenomenon. This can sometimes be observed at the start of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias or in a long-short sequence in which the refractory period of the long sequence is prolonged. This is also called Ashman phenomenon.
Phase 4 Aberration or deceleration dependant
Phase 4 aberration only occurs after prolonged pause. During such a pause (e.g. in second degree AV block) the Purkinje fibers can depolarize spontaneously. As their membrane potential becomes more positive, the conduction velocity decreases and can even be blocked altogether. This is usually a pathological response, but can be normal at very low heart rates (e.g. 40 bpm)
Acceleration dependant
A small increase in rhythm resulting in aberrancy due to an abnormal response of tissue that has diminished excitability.
Retrograde Concealed Conduction
This is the most common mechanism for sustained aberrancy during tachycardia. The sequence of QRS widening that is often observed is phase 3 aberration in the first premature beat. This can leave the left bundle (for example) refractory for the next complex. This next beat is conducted by the right bundle and once it reaches the apex, it is conducted retrograde by the left bundle. This can continue until a new premature ventricular complex causes a compensatory pause and 'resets' the system.
Fixed Bundle Branch Block

Complete or marked conduction delay in a bundle branch leading to complete ventricular activation over the contralateral bundle branch.
{{{1}}}